ImageMethods¶
-
class
imgreg.util.methods.ImageMethods[source]¶ Bases:
objectCollection of static methods for image analysis and manipulation.
Methods
__init__(*args, **kwargs)Initialize self.
abs_diff(image, ref_image)Absolute value of the difference between two images.
compute_afts(image)Compute FFT magnitude, shifted with low fequencies in center.
compute_dgfw(image[, gaussdiff, …])Image Difference of Gaussian Filter + Window.
compute_log_polar_tf(image[, wrexp, order])Compute log-scaled polar coordinate transform of center shifted FFT.
compute_rts(image[, angle, scale, …])Rotate, translate and scale image.
compute_warp_radius(image_diameter[, wrexp])Compute the warp radius from image and warp radius exponent wrexp.
exp_filter(image[, signal_noise_ratio])Remap the values of the image such that bright pixels are given an exponentially higher weight.
max_sinogram_angle(image[, theta, …])Iterative solver, works well in special cases.
norm_rel_l2(image, ref_image)Compute a relative similarity measurement between two images.
recover_rs(image_warped_fs, rts_warped_fs, …)Recover the rotation and scaling transformation from given input.
sinogram(image[, theta, exp_filter_val, circle])Computes the radon transformation and optionally applies the exp_filter afterwards.
sinogram_project(image[, theta, …])Projects the sinogram onto the axis of the theta angle.
sqr_diff(image, ref_image)Squared difference between two images.
-
static
abs_diff(image: numpy.ndarray, ref_image: numpy.ndarray) → numpy.ndarray[source]¶ Absolute value of the difference between two images.
Notes
-
static
compute_afts(image: numpy.ndarray) → numpy.ndarray[source]¶ Compute FFT magnitude, shifted with low fequencies in center.
- Parameters
- imagenumpy.ndarray
The input image for the fourier transform
- Returns
- numpy.ndarray
FFT magnitude, center shifted
-
static
compute_dgfw(image: numpy.ndarray, gaussdiff: Sequence[float] = (5, 20), windowweight: float = 1, windowtype: str = 'hann') → numpy.ndarray[source]¶ Image Difference of Gaussian Filter + Window.
- Parameters
- imagenumpy.ndarray
The input image to filter
- gaussdiff(float, float), optional
The low and high standard deviations for the gaussian difference band pass filter
- windowweightfloat, optional
weighting factor scaling beween windowed image and image
- windowtypestr, optional
see skimage.filters.window for possible choices
- Returns
- numpy.ndarray
modified image with bandpass filter and window applied
Notes
Applying this bandpass and window filter prevents artifacts from image boundaries and noise from contributing significantly to the fourier transform. The gaussian difference filter can be tuned such that the features relevant for the identification of the rotation angle are at the center of the band pass filter.
-
static
compute_log_polar_tf(image: numpy.ndarray, wrexp: float = 3, order: int = 5) → numpy.ndarray[source]¶ Compute log-scaled polar coordinate transform of center shifted FFT.
- Parameters
- imagenumpy.ndarray
The input image to transform (expects center shifted FFT magnitude)
- wrexpfloat, optional
Cutoff exponent factor for higher frequencies, larger wrexp => faster computation min value: 1
- Returns
- numpy.ndarray
log-scaled polar transformed of the input image
-
static
compute_rts(image: numpy.ndarray, angle: float = 0, scale: float = 1, translation: Sequence[float] = (0.0, 0.0), inverse: bool = False, preserve_range: bool = True, order: int = 5) → numpy.ndarray[source]¶ Rotate, translate and scale image.
- Parameters
- imagenumpy.ndarray
The input image to transform
- anglefloat, optional
The rotation angle in degrees for the transform
- scalefloat, optional
The scaling factor used in the transform
- translation(float, float), optional
x,y-translations used in the transform
- inversebool
Apply the backwards transformation for given parameters
- Returns
- numpy.ndarray
modified image with same shape as initial image
-
static
compute_warp_radius(image_diameter: int, wrexp: float = 1.0) → int[source]¶ Compute the warp radius from image and warp radius exponent wrexp.
- Parameters
- image_diameterint
The length of the smallest image dimension
- wrexpfloat, optional
Cutoff exponent factor for higher frequencies, larger wrexp => faster computation min value: 1
- Returns
- int
The cutoff radius for the log-ploar transform of the image
-
static
exp_filter(image: numpy.ndarray, signal_noise_ratio: Optional[float] = None) → numpy.ndarray[source]¶ Remap the values of the image such that bright pixels are given an exponentially higher weight.
Maps the min value of the input image to 1/signal_noise_ratio and the max value to 1.
-
static
max_sinogram_angle(image, theta=None, exp_filter_val=None, circle=False, precision=0.1) → float[source]¶ Iterative solver, works well in special cases. Implementation very crude.
-
static
norm_rel_l2(image: numpy.ndarray, ref_image: numpy.ndarray) → float[source]¶ Compute a relative similarity measurement between two images.
Interpretes the images as a vector and calculates the L2 norm of the differences relative to the reference image ref_image.
Notes
L2 norm Implemented analog to NormRel_L2 1.
Where
denotes the Frobenius norm of a matrix.
References
-
static
recover_rs(image_warped_fs: numpy.ndarray, rts_warped_fs: numpy.ndarray, image_shape: Sequence[int], upsampl: int = 10, wrexp: float = 3) → Tuple[numpy.ndarray, numpy.ndarray, Dict[str, Hashable]][source]¶ Recover the rotation and scaling transformation from given input.
- Parameters
- image_warped_fsnp.ndarray
log-polar warped fourier transformed of original input image
- rts_warped_fsnp.ndarray
log-polar warped fourier transformed of modified input image
- image_shapeSequence[int]
image dimensions of original input image
- upsamplint, optional
Upsampling factor. 1 => no upsampling, 20 => precision to 1/20 of a pixel
- wrexpfloat, optional
Cutoff exponent factor for higher frequencies, larger wrexp => faster computation min value: 1
- Returns
- numpy.ndarray
Vector of recovered rotation angle and error in degrees
- numpy.ndarray
Vector of recovered scaling factor and error
- dict
Dict containing the phase_cross_correlation parameters
Notes
The errors are a lower estimate under ideal assumptions and can be much larger depending on the data.
-
static
sinogram(image, theta=None, exp_filter_val=None, circle=False) → numpy.ndarray[source]¶ Computes the radon transformation and optionally applies the exp_filter afterwards.
Examples
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import imgreg.data as data from imgreg.util.methods import ImageMethods img = np.array(data.mod_img()) # Compute the sinogram using the radon transform sinogram = ImageMethods.sinogram(img) plt.imshow(sinogram, aspect=0.1) plt.show()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
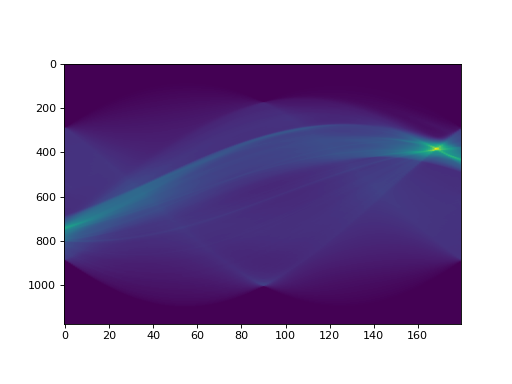
# Compute the same sinogram but apply an exponential weighting filter sinogram = ImageMethods.sinogram(img, exp_filter_val=1000) plt.imshow(sinogram, aspect=0.1) plt.show()
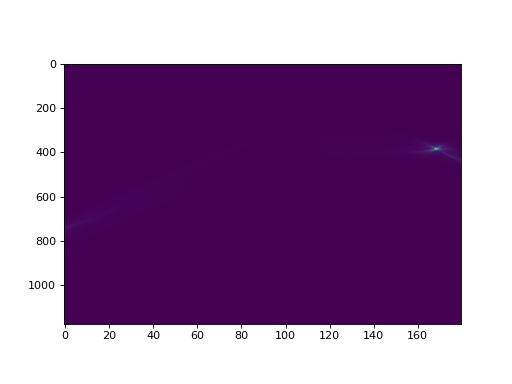
-
static
sinogram_project(image, theta=None, exp_filter_val=None, circle=False) → numpy.ndarray[source]¶ Projects the sinogram onto the axis of the theta angle.
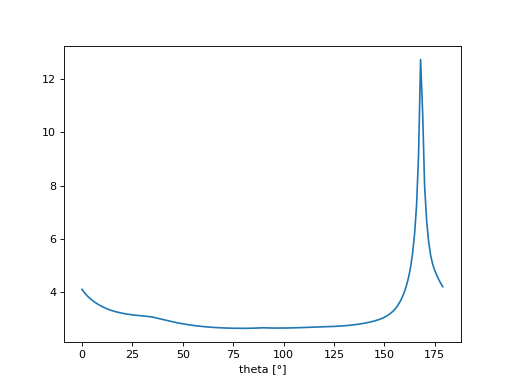
Examples
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import imgreg.data as data from imgreg.util.methods import ImageMethods img = np.array(data.mod_img()) # Compute the sinogram with the exponential weighting filter and project the image values # to the axis corresponding to the theta angles. sinogram_project = ImageMethods.sinogram_project(img, exp_filter_val=1000) plt.plot(sinogram_project) plt.xlabel("theta [°]") plt.show()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
-
static